True/False
Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true
or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
The
speed of light in water is 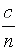 , where n = 1.33
is the index of refraction of water. The speed of light in water is thus less than the speed of light
in a vacuum. This fact violates the speed-of-light postulate of the special theory of
relativity. , where n = 1.33
is the index of refraction of water. The speed of light in water is thus less than the speed of light
in a vacuum. This fact violates the speed-of-light postulate of the special theory of
relativity.
|
|
|
2.
|
We
customarily say that Earth revolves around the Sun. We can also say that the Sun revolves around
Earth.
|
|
|
3.
|
If
events E1 and E2 are simultaneous in an inertial frame, then no observers
stationary in the same frame will regard E1 as occurring before
E2.
|
|
|
4.
|
Any
two observers moving with a clock will agree on the rate at which it ticks.
|
|
|
5.
|
Any
two observers moving relative to each other, and simultaneously moving relative to a clock, will
agree on the rate at which the clock ticks.
|
|
|
6.
|
An
observer moving with a clock, measuring the time between ticks, measures the proper time between
ticks.
|
|
|
7.
|
Earth
rotates on its axis once each day. To a person observing Earth from an inertial frame of reference in
space, that is, stationary relative to Earth, a clock runs slower at the North Pole than at the
equator. (Ignore the orbital motion of Earth about the Sun.)
|
|
|
8.
|
A
young astronaut has just returned to Earth from a long mission. She rushes up to an old man and in
the ensuing conversation refers to him as her son. She cannot possibly be addressing her
son.
|
|
|
9.
|
An
object will be greater in length if the observer is moving with the object than if the object is
moving relative to the observer.
|
|
|
10.
|
An
observer at rest relative to a moving object measures the object’s proper length.
|
|
|
11.
|
Relativistic effects such as time dilation and length contraction are for practical
purposes undetectable in automobiles.
|
|
|
12.
|
The
total relativistic energy of an object is always equal to or greater than its rest mass
energy.
|
|
|
13.
|
Since
rest mass is a form of energy, a spring has more mass when the coils are compressed than when
relaxed.
|
|
|
14.
|
The
classical laws of conservation of energy and conservation of mass do not need to be modified for
relativity.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
15.
|
You are in a
windowless spacecraft. You need to determine whether your spaceship is moving at constant nonzero
velocity, or is at rest, in an inertial frame of Earth. a. | You can succeed by
making very precise time measurements. | b. | You can succeed by making very precise mass
measurements. | c. | You can succeed by making very precise length and time
measurements. | d. | You cannot succeed no matter what you do. | e. | You are in a position
not correctly described by any of these propositions. | | |
|
|
|
16.
|
You and your
friend recede from each other in spacecraft in deep space without acceleration. In an inertial frame
on your spaceship, your friend is receding at a speed of 0.9999c. If you direct a light beam
at your friend, and your friend directs a light beam at you, then a. | neither beam will reach
the ship to which it is directed | b. | you will see your friend’s light arrive at a speed of 2c,
and your friend will see your light arrive at a speed of 2c | c. | you will see your
friend’s light arrive at a speed of c, and your friend will see your light arrive at a
speed of c | d. | one of you will see light arrive at a speed of c, and the other
will see light arrive at 2c | e. | none of these propositions is true | | |
|
|
|
17.
|
Simultaneity
is a. | dilated | b. | absolute | c. | invariant | d. | relative | e. | none of these | | |
|
|
|
18.
|
The
Michelson–Morley experiment established that a. | there is no observable ether wind at the surface of
Earth | b. | the ether moves at c as Earth travels in its
orbit | c. | the ether is an elastic solid that streams over
Earth | d. | Earth does not move with respect to the Sun | e. | none of
these | | |
|
|
|
19.
|
A Klingon
spaceship is approaching Earth at approximately 0.8c measured relative to Earth. The spaceship
directs a laser beam forward directly through your physics classroom window. You measure the speed of
this light to be a. | 1.8c | b. | 1.0c | c. | 0.9c | d. | 0.8c | e. | 0.2c | | |
|
|
|
20.
|
You are an
astronaut heading out toward a star. In the inertial frame of the star, you are steering directly for
the star and are moving at constant speed. You can determine that you are in motion
by a. | the slowing down of
on-board clocks | b. | the contraction of on-board metre sticks | c. | your increase in
mass | d. | the increase in your
heart rate | e. | none of these | | |
|
|
|
21.
|
A clock,
designed to tick each second, is moving past you at a uniform speed. You find the moving clock
to be a. | ticking slowly | b. | ticking
quickly | c. | accurate | d. | running backward | e. | none of
these | | |
|
|
|
22.
|
The proper
time between events E1 and E2 is a. | the time measured on
clocks at rest with respect to E1 and E2 | b. | the time measured on
clocks at rest in an inertial system moving properly with respect to E1 and
E2 | c. | the time measured on clocks moving uniformly with respect to
E1 and E2 | d. | the time between E1 and E2 as measured by a
clock in a national-standards laboratory, such as the National Research Council in
Ottawa | e. | none of these | | |
|
|
|
23.
|
There are
about 2.81 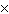 109 heartbeats in an average lifetime of 72
years. Space travellers who are born and die on a spaceship moving at a constant speed of
0.600c can expect their hearts to beat a total of 109 heartbeats in an average lifetime of 72
years. Space travellers who are born and die on a spaceship moving at a constant speed of
0.600c can expect their hearts to beat a total of a. | (0.600)(2.81 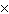 109) times 109) times | b. | 2.81 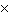 109 times 109 times | c. | (0.800)(2.81 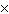 109)
times 109)
times | d. | (1.25)(2.81 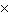 109)
times 109)
times | e. | none of these | | |
|
|
|
24.
|
A
mass–spring system oscillates up and down with a period T when stationary in the inertial
frame of an Earthbound observer. The same system is then moved past the Earthbound observer, with a
velocity which in the observer’s frame is constant and of magnitude 0.50c. The observer
now determines the period to be a. | 0.50T | b. | 0.87T | c. | 1.0T | d. | 1.2T | e. | 2.0T | | |
|
|
|
25.
|
According to
the effects of length contraction, from the viewpoint of an observer stationary with respect to a
body moving at a uniform speed relative to the observer, a. | the body is not now
contracted but would contract if it were to accelerate | b. | the body contracts
along the direction of motion | c. | the time it takes for a clock incorporated in the body to tick
contracts | d. | the body contracts in some direction transverse to the direction of
its motion | e. | none of these | | |
|
|
|
26.
|
The energy
output of the Sun is 3.7 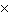 1026 J/s. Matter is converted to energy in
the Sun at the rate of 1026 J/s. Matter is converted to energy in
the Sun at the rate of a. | 4.1 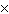 109
kg/s 109
kg/s | b. | 6.3 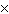 109 kg/s 109 kg/s | c. | 7.4 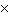 101
kg/s 101
kg/s | d. | 3.7 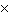 109 kg/s 109 kg/s | e. | none of these | | |
|